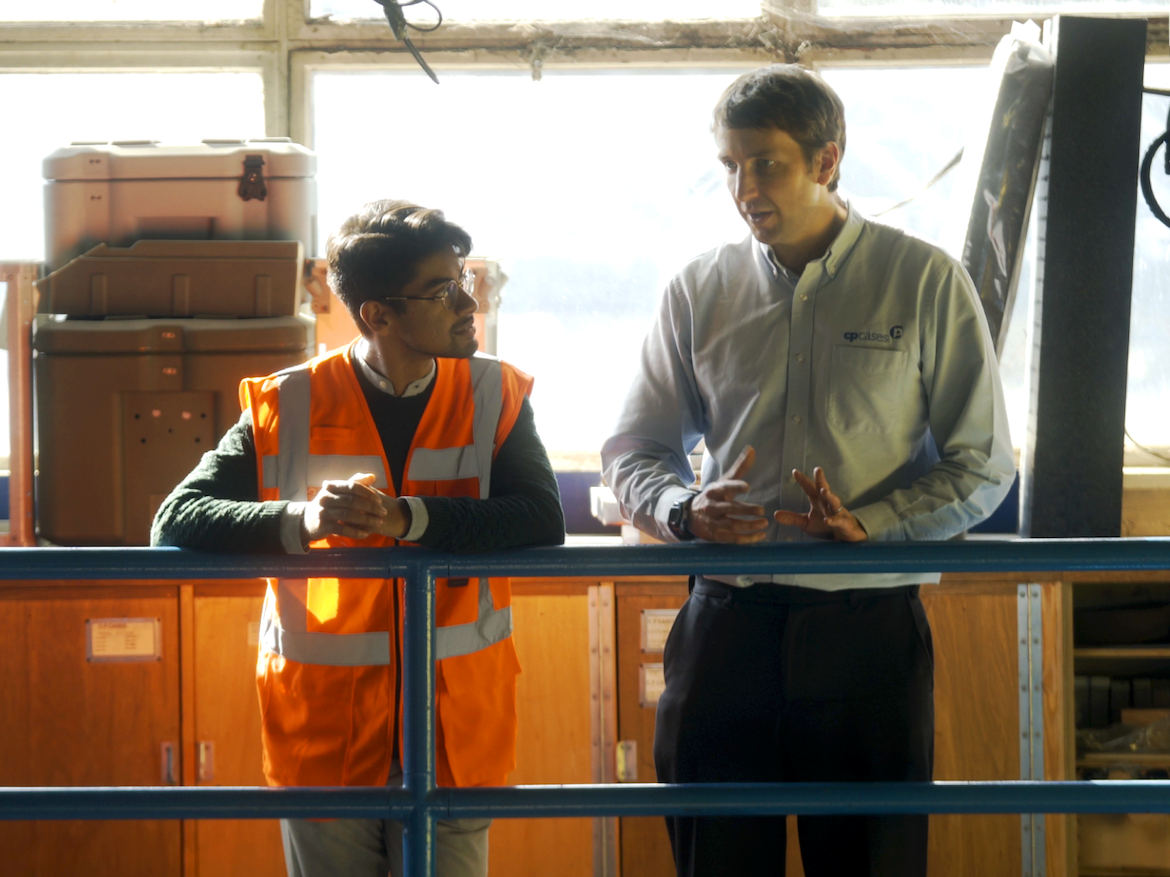
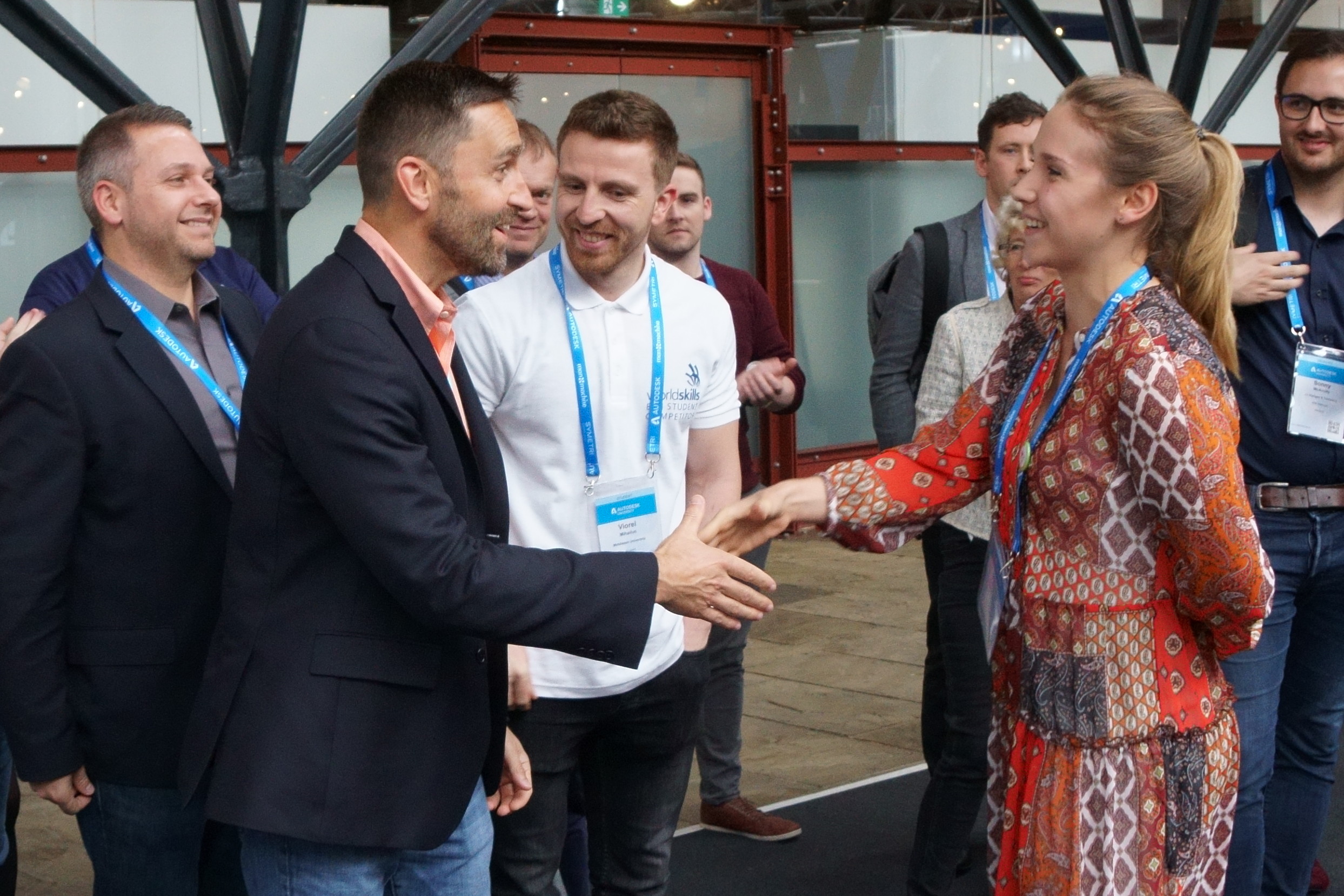
On the second day of Autodesk University London, Lisa Campbell, Autodesk’s Chief Marketing Officer, delivered an insightful presentation on how the company is working to shape a better and more promising future of work in the age of automation. The global skills gap is one of the most pressing challenges facing industries today. While millions of jobs remain unfilled, there are also millions of people seeking employment. According to the World Economic Forum, while 75 million jobs may be displaced by automation by 2022, 133 million new roles will emerge—resulting in a net gain of 58 million jobs worldwide. This highlights a growing need for upskilling rather than a lack of job opportunities. Workers must now adapt to a rapidly evolving digital landscape, where collaboration with machines becomes essential. While AI, robotics, and automation are often seen as threats, they can also be powerful tools for progress—if used thoughtfully. The key lies in ensuring that automation enhances opportunities rather than limiting them. The integration of design and manufacturing is reshaping the industry. In the UK, these two sectors combined support nearly 4 million jobs. By bridging the gap between design and manufacturing, we unlock new potential for innovation and efficiency. This synergy represents a new era of agile production and creative problem-solving. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play a crucial role in this transformation. However, many struggle with limited resources and difficulty in attracting skilled talent. Last year alone, over 59,000 manufacturing jobs went unfilled in the UK, while only 34,000 students were enrolled in relevant degree programs. This mismatch calls for innovative solutions to close the skills gap. Asif Moghal, a senior industry manager at Autodesk, has been working closely with UK SMEs to address this challenge. He emphasizes the importance of digital natives entering the workforce, who bring fresh perspectives and the potential to drive change. To support this, Autodesk launched the Digital Catalyst program, part of its Future of British Manufacturing Initiative. The program aims to place students in SMEs, fostering collaboration between education and industry. Last year, Umar Hossain, a PhD student from Imperial College, was placed at CP Cases through the program. His work significantly improved their additive manufacturing process, reducing a time-consuming task from 180 minutes to just 15. This kind of impact demonstrates the value of bridging the gap between academia and industry. In addition to its own initiatives, Autodesk has partnered with the Monitor Institute—a division of Deloitte—to explore the root causes of the skills gap and identify strategies to help workers thrive in the digital age. Their research offers valuable insights into how industries can prepare for the future and ensure that no one is left behind. Autodesk is also collaborating with WorldSkills International to equip students with the skills needed for the future workplace. The WorldSkills Competition brings together young talents from around the globe, showcasing their abilities in over 45 different skills—including those using Autodesk tools. In the AEC sector, the shift toward digital construction has created new job roles requiring expertise in BIM modeling and data management. To reflect this change, WorldSkills recently introduced a BIM competition, where students use Autodesk Revit and BIM 360 to demonstrate real-world competencies. This year, Autodesk University London hosted the regional BIM competition for the first time, featuring 10 top students from London Southbank University, Middlesex University, and Oxford Brookes University. Industry experts from JJ Rhatigan and Baker Hicks judged the event, highlighting the importance of these skills in modern construction. Barbara Adamska from Oxford Brookes emerged as the top scorer in the competition. Her performance demonstrated not only technical skill but also the potential to shape the future of the industry. Barbara Adamska from Oxford Brookes achieved the highest score in the regional WorldSkills BIM competition. While we cannot control every aspect of the future, we can influence many of the outcomes. That’s why Autodesk is taking a multi-faceted approach—through programs, research, and continuous learning—to ensure our tools empower professionals at every stage of their careers. This is the future of agile design, construction, and manufacturing.
PC film is the abbreviation of polycarbonate film, which is an amorphous, odorless, non-toxic, highly transparent colorless or yellowish thermoplastic engineering plastic.
advantage Pc Film,Pc Sheet Film,White Pc Film,Printing Pc Film Shandong Top Leader Plastic Packing CO., LTD , https://www.sdzlplastic.com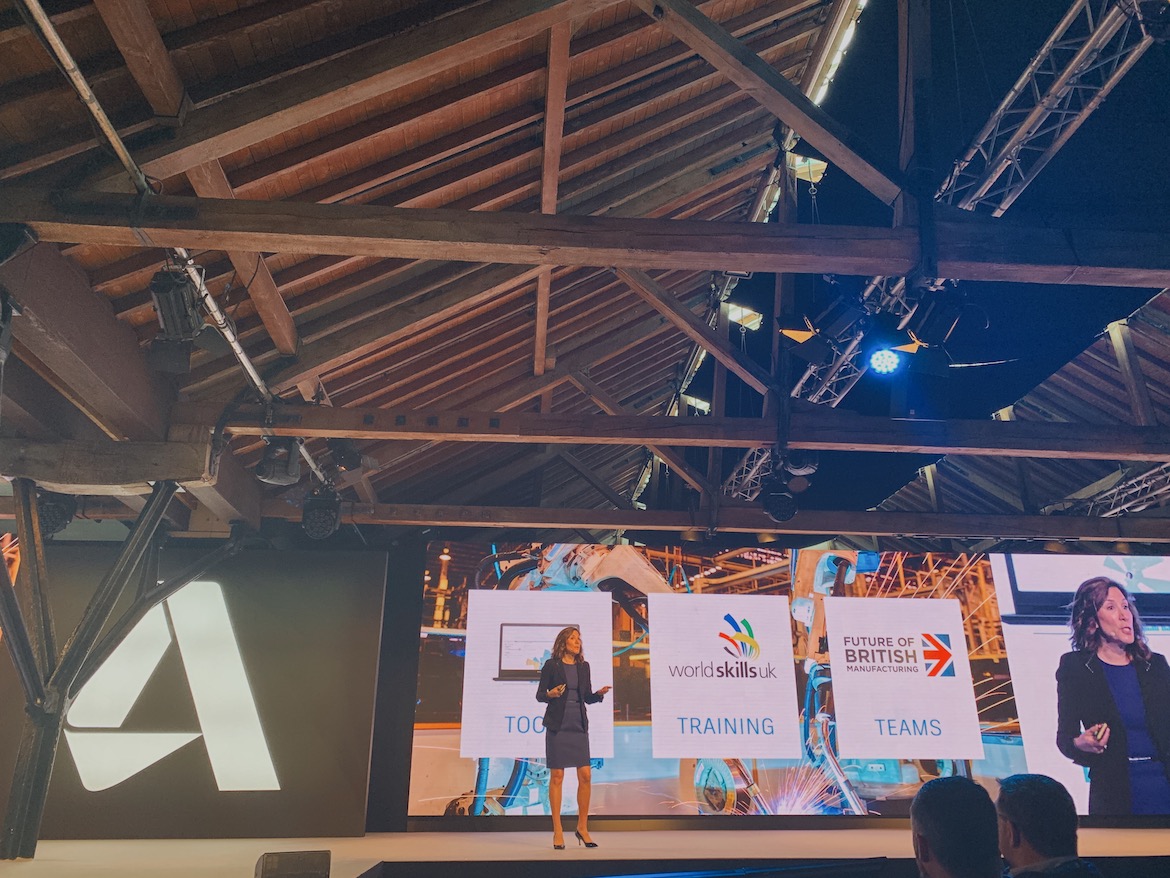
Catalysts for Change

Unlocking the Power of Data
Empowering the Next Generation

It has excellent physical and mechanical properties, especially excellent impact resistance, high tensile strength, bending strength, and compression strength; good heat resistance and low temperature resistance, stable mechanical properties in a wide temperature range, and size Stability, electrical properties and flame retardancy, can be used for a long time at -60~120℃; no obvious melting point, in a molten state at 220-230℃; high rigidity, high resin melt viscosity; low water absorption, low shrinkage , Small creep, high dimensional accuracy, good dimensional stability, low permeability of the film; self-extinguishing material; stable to light, but not resistant to ultraviolet light, good weather resistance; oil and acid resistance.
Disadvantage
The fatigue strength is poor, stress cracking easily occurs, and the wear resistance is poor. Poor resistance to solvents, not resistant to strong alkalis, oxidizing acids, amines and ketones, soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents, and prone to hydrolysis and cracking in water for a long time.
pc film classification
PC films are divided into: halogen-free flame-retardant PC, black flame-retardant PC, transparent flame-retardant PC, frosted PC, transparent PC, hardened PC, scratch-resistant PC, scratch-resistant PC, printing-grade PC, optical-grade PC
pc film use
1. Flame-retardant pc film is used for power system insulation, disk drive insulation, keyboard insulation, TV/display insulation, and computer motherboard insulation. It is widely used in electronic components, electrical enclosures, switch panels, junction boxes and charger enclosures, automotive instrumentation and panel printing with flame-retardant requirements.
2. Printing grade frosted pc film is suitable for special printing, helmets, signs, nameplates, protective covers, etc.
3. Anti-scratch pc film Uses: window lenses for mobile phones, MP3, MP4, DVD, backlight and other electronic products